ASA Maestro online Help
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |
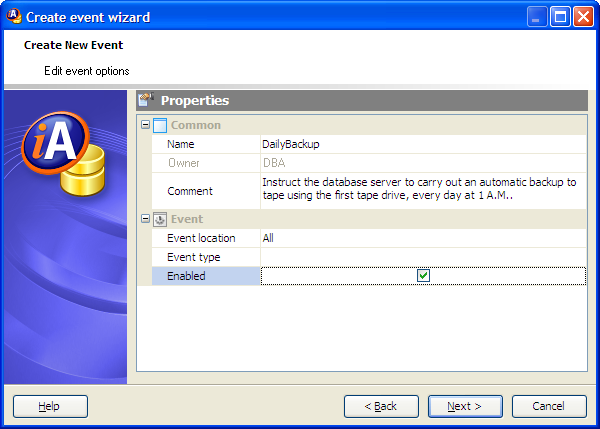
Setting event properties
This step is provided for specifying the new event properties in the most convenient way.
Name
The field contains the new scheduled event name as it was set on the previous step.
Comment
Specify a comment to the event or leave it blanc.
Event location (Consolidated, Remote, All)
If you want to execute events at remote or consolidated databases in a SQL Remote setup, you can use this clause to restrict the databases at which the event is handled. By default, all databases execute the event.
Event type
Select the event type from the listed set of system-defined event types.
server idle (ServerIdle): If the database contains an event handler for the event type, the database server checks for server activity every 30 seconds.
If the database contains an event handler for one of the Disk Space types, the database server checks the available space on each device associated with the relevant file every 30 seconds. Such event types are not supported on Windows CE.
- database disk space checked (DBDiskSpace): In the event the database has more than one dbspace, on separate drives, the event checks each drive and acts depending on the lowest available space.
- transaction log disk space checked (LogDiskSpace): The event type checks the location of the transaction log and any mirrored transaction log, and reports based on the least available space.
- temporary file disk space checked (TempDiskSpace): The event type checks the amount of temporary disk space.
If the appropriate event handlers have been defined (DBDiskSpace, LogDiskSpace, or TempDiskSpace), the database server checks the available space on each device associated with a database file every 30 seconds. Similarly, if an event has been defined to handle the system event type server idle (ServerIdle), the database server notifies the handler when no requests have been process during the previous 30 seconds.
- global autoincrement near end of range (GlobalAutoincrement): The event fires on each insert when the number of remaining values for a GLOBAL AUTOINCREMENT is less than 1% of the end of its range. A typical action for the handler could be to request a new value for the global_database_id option, based on the table and number of remaining values which are supplied as parameters to this event.
- mirror server disconnected (MirrorServerDisconnect), mirror failover (MirrorFailover) The MirrorServerDisconnect event fires when a connection from the primary database server to the mirror server or arbiter server is lost, and the MirrorFailover event fires whenever a server takes ownership of the database.
- backup completed (BackupEnd): You can use the event type to take action at the end of a backup.
- database started (DatabaseStart): You can use the event type to take action when a database is started.
- user connected ("Connect"), connect failed (ConnectFailed): Connection events When a connection is made (Connect) or when a connection attempt fails (ConnectFailed). You may want to use these events for security purposes. As an alternative to a connect event handler, you may want to consider using a login procedure.
- user disconnect ("Disconnect"): You can use the event to take action when a user or application disconnects.
- database file extended (GrowDB), transaction log extended (GrowLog), temporary file extended (GrowTemp): The file reaches a specified size. This can be used for the database file (GrowDB), the transaction log (GrowLog), or the temporary file (GrowTemp).
- RAISERROR issued ("RAISERROR") When an error is triggered, you can use the RAISERROR event type to take actions.
Enabled
Uncheck the option to keep the event been created from being active.
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |




 Download
Download Buy
Buy