PostgreSQL Maestro online Help
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |
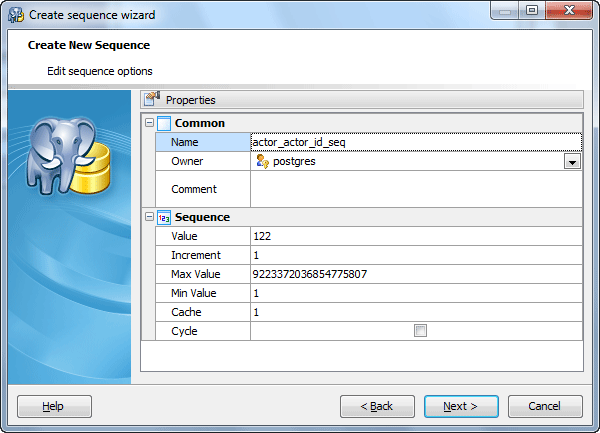
Create Sequence Wizard
Sequences may be created with Create Sequence Wizard. Just specify the wizard options according to your needs.
The basic principles of Create Object Wizards in PostgreSQL Maestro are explained in a separate topic. Below you will find a description of wizard steps that are unique for the current object.
Name
The field allows you to specify the new sequence name being set on the previous wizard step.
Owner
Defines the owner of the new sequence.
Increment
Specify which value is added to the current sequence value to create a new value. A positive value will make an ascending sequence, a negative one a descending sequence. The default value is 1.
Max Value
Determine the maximum value for the sequence. If this clause is not supplied or NO MAXVALUE is specified, then default values will be used. The defaults are 2^63-1 and -1 for ascending and descending sequences, respectively.
Min Value
Determine the minimum value a sequence can generate. If this clause is not supplied or NO MINVALUE is specified, then defaults will be used. The defaults are 1 and -263-1 for ascending and descending sequences, respectively.
Cashe
Specify how many sequence numbers are to be preallocated and stored in memory for faster access. The minimum value is 1 (only one value can be generated at a time, i.e., no cache), and this is also the default.
 Cycle
Cycle
The CYCLE option allows the sequence to wrap around when the maxvalue or minvalue has been reached by an ascending or descending sequence respectively. If the limit is reached, the next number generated will be the minvalue or maxvalue, respectively.
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |





 Download
Download Buy
Buy