Oracle Maestro online help
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |
Editing properties
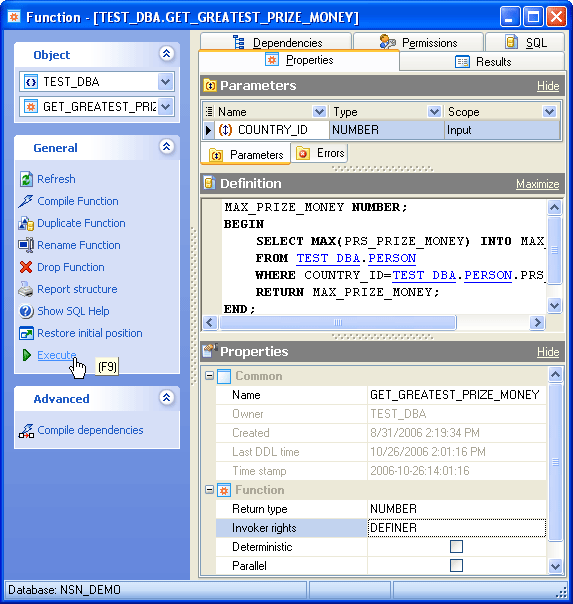
The Parameters tab contains the list of the current Function parameters with its options. Here you can view the Name and the Type of each Function parameter and also view it's Scope
Parameters can be edited within the Parameter Editor dialog window. In order to open the dialog you should
| • | open the object in its editor and the Parameters tab there; |
| • | select the parameter to edit; |
| • | press the Enter key or select the Edit Parameter item from the popup menu (alternatively, you may use the corresponding link of the Navigation Bar). |
The Errors tab displays all the necessary information about object errors. If an error have occurred during the object compilation it appears in the list with some additional properties: Order (one after another), Line and Position (object definition location the error was found out), Error (corresponding PL/SQL exception).
The Definition field contains the definition of the Function. Specify a string constant defining the Function here; the meaning depends on the language. It may be an internal Function name, the path to an object file, an SQL command or text in a procedural language.
Name
You can edit the Function name here. The name of the Function must be unique among all the Function names in the database.
Owner
The field contains the owner of the Function.
Created
The field displays the date the object was created.
Last DDL time
Use the field to find the date when the last data definition language (DDL) operation was performed on the current object. The Last DDL time can help you to find if any changes to the object definitions have been made on or after a specific time.
Return type
The field defines the data type of the function result.
Invoker rights (DEFINER, CURRENT USER)
Specify DEFINER to indicate that the procedure executes with the privileges of the owner of the schema in which the procedure resides, and that external names resolve in the schema where the procedure resides. Specify CURRENT USER to indicate that the procedure executes with the privileges of CURRENT USER. This clause also specifies that external names in queries, DML operations, and dynamic SQL statements resolve in the schema of CURRENT USER. External names in all other statements resolve in the schema in which the procedure resides.
 Deterministic
Deterministic
Check the box to indicate that the function returns the same result value whenever it is called with the same values for its arguments
 Parallel
Parallel
The option indicates that the function can be executed from a parallel execution server of a parallel query operation. The function should not use session state, such as package variables, as those variables are not necessarily shared among the parallel execution servers.
To apply the changes, select the Apply Changes item in the Navigation bar or use Ctrl+F9 or Ctrl+F7 shortcut keys.
It is also possible to modify object properties without opening the object editor: use the Object Properties item of the popup menu of the selected object from the explorer tree.
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |





 Download
Download Buy
Buy