Oracle Maestro online help
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |
Setting index properties
The Index Properties dialog is available from Create Table Wizard, Table Editor, or from corresponding nodes of the Explorer tree.
Use the Columns drop-down list to select a key field(s) for the index.
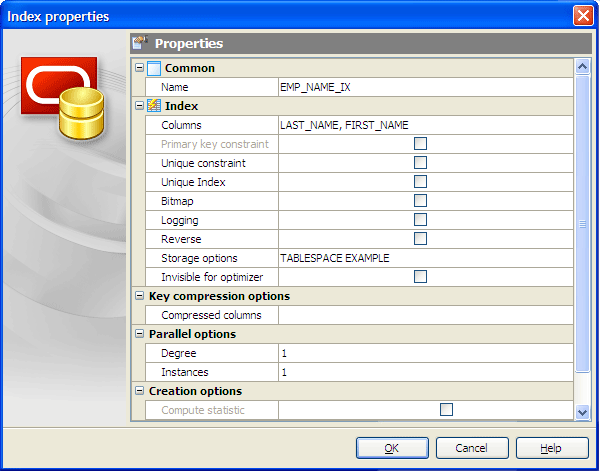
 Primary key constraint
Primary key constraint
With this option checked this field becomes a compound primary key. It is useful in case the table has more than one primary key.
 Unique constraint
Unique constraint
Check the option to permit no duplicate values. A unique column must also define the NOT NULL attribute. A table can have one or more unique keys.
 Unique Index
Unique Index
If checked, creates a unique index for the table, i.e. the database system ensures that no two rows of the specified table have the same values in the indexed columns. In this way, if two rows both contain the NULL value for all columns of an index, the two index values are not considered to be identical. If at least one column does not contain the NULL value, two rows that have the same value in all non-NULL columns are considered to be identical.
Bitmap
Use the checkbox to set storing rowids associated with a key value as a bitmap.
Logging
Specify whether the creation of the index will be logged (LOGGING) or not logged (NOLOGGING) in the redo log file. This setting also determines whether subsequent Direct Loader (SQL*Loader) and direct-path INSERT operations against the index are logged or not logged. LOGGING is the default.
Reverse
Specify the clause to store the bytes of the index block in reverse order, excluding the rowid.
You can also define Storage options here.
Compressed columns
Specify compression value to enable key compression, which eliminates repeated occurrence of key column values and may substantially reduce storage. Use integer to specify the prefix length (number of prefix columns to compress).
Use the Parallel options to parallelize creation of the domain index. For a nonpartitioned domain index, Oracle Database passes the explicit or default degree of parallelism to the ODCIIndexCreate cartridge routine, which in turn establishes parallelism for the index.
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |





 Download
Download Buy
Buy