PHP Generator for MySQL online Help
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |
How to connect to MySQL
Connection properties
Specify the connection parameters for a database you want PHP Generator for MySQL to work with.
Script connection properties
These parameters will be used by the generated web application. By default they are the same as parameters used by PHP Generator for MySQL but you can change them if necessary. For example, if you are working with a remote database located at your web hosting and your database server and web server are installed on the same computer, you have to specify the value of the Host parameter as localhost.
PHP Generator for MySQL allows you to connect to MySQL databases directly, or via Secure SHell (SSH) tunnel or HTTP tunnel.
| • | Direct connection |
It is the most natural and the most preferable connection mode. Use it each time it is possible. Most of hosting companies allow direct connections to databases. However in most cases you have to go to your control panel and add your home/office computer IP address or domain name to the Access List - list of IP addresses allowed accessing from outside. More information.
| • | SSH tunnel connection |
If your MySQL server does not allow direct connections from your remote workstations, you can establish connection to an allowed intermediate SSH server and forward all MySQL commands through the Secure SHell (SSH) tunnel.
| • | HTTP tunnel connection |
HTTP tunneling is a technique used in conditions of restricted network connectivity including firewalled networks, networks behind proxy servers, and NATs. It is the slowest way and is recommended to use if the others are impossible.
Irrespectively of a connection mode you should specify common credentials as follows:
Host
The host name of the MySQL server.
Port number
The TCP/IP port to use (default MySQL port is 3306).
User name
The username used to connect to MySQL.
Password
The password for the user account on server.
Allow old style password
Turn this option ON only if your MySQL server still uses 16 bytes long password hashes. More information.
 More about SSH tunnel connection
More about SSH tunnel connection
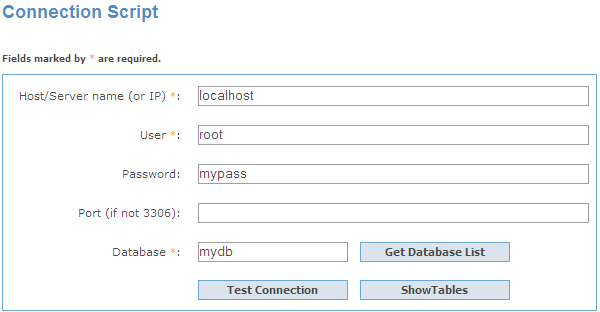
To establish connection to intermediate SSH server and forward all MySQL commands through the secure tunnel, you need to:
Host name Specify the host name or IP of your site. Note, that MySQL host name always should be set relatively to the SSH server. For example, if both of MySQL and SSH servers are located on the same computer, you should specify localhost as Host name instead of server's external host name or IP address.
Port number Enter the port number for the SSH server. 4. Enter valid User name for the remote server and select the Authentication method and set corresponding credentials.
Password-based Set the password corresponding to the specified user.
Key-based Specify the path to the Private key file with the corresponding Passphrase to log in to the remote server. PHP Generator for MySQL accepts keys in ssh.com or OpenSSH formats. To convert a private key from PuTTY's format to one of the formats supported by our software, use the PuTTYgen utility that can be freely downloaded from the PuTTY website.
Keyboard interactive Keyboard authentication is the advanced form of password authentication, aimed specifically at the human operator as a client. During keyboard authentication zero or more prompts (questions) is presented to the user. The user should give the answer to each prompt (question). The number and contents of the questions are virtually not limited, so certain types of automated logins are also possible. |
 More about connection via HTTP tunnel
More about connection via HTTP tunnel
To connect to a remote server using an HTTP tunnel, you need to:
Note: You are actually connecting to your database through the PHP script on the server, so in most cases the host/server name is "localhost" unless the target database server is not installed on the same computer as the Web server. |





 Download
Download Buy
Buy