SQL Maestro for MySQL online help
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |
Foreign Keys
A foreign key is a field (or collection of fields) in one table that uniquely identifies a row of another table. In other words, a foreign key is a column or a combination of columns that is used to establish and enforce a link between the data in two tables.
Note: To create a foreign key constraint, it is necessary to have this privilege for both the referencing and referenced tables.
Foreign keys are created within the Foreign Key Properties dialog window. In order to open the dialog you should either
or
or
|
Foreign Keys are edited within the Foreign Key Properties dialog window. In order to open the dialog you should either
or
You can change the name of the foreign key using the Rename Foreign Key dialog. To open the dialog you should either
or
|
To drop the foreign key:
or
and confirm dropping in the dialog window.
|
Set the Foreign Key Name, select Columns from the Available Fields list to include into the foreign key, select the Foreign Table Name from the drop-down list and its fields from the list to include, set other foreign key properties and apply the changes by clicking the OK button.
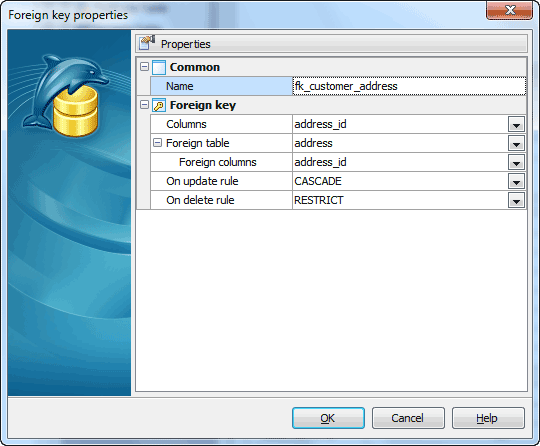
All the fields which are included into the Foreign Key must be included into indexes as well. See Indexes for details.
Set rules ON DELETE and ON UPDATE from the respective drop-down lists.
| • | NO ACTION Produce an error indicating that the deletion or update will create a foreign key constraint violation. If the constraint is deferred this error will be produced at constraint check time if there still exist any referencing rows. This is the default action. |
| • | RESTRICT Produce an error indicating that the deletion or update would create a foreign key constraint violation. |
| • | CASCADE Delete any rows referencing the deleted row, or update the value of the referencing column to the new value of the referenced column, respectively. |
| • | SET NULL Set the referencing column(s) to null. |





 Download
Download Buy
Buy