MS SQL Maestro online Help
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |
Certificate login options
Certificate logins were implemented in Microsoft SQL server 2005.
This step of the wizard allows you to specify Certificate login options according to your needs. The detailed description is given below.
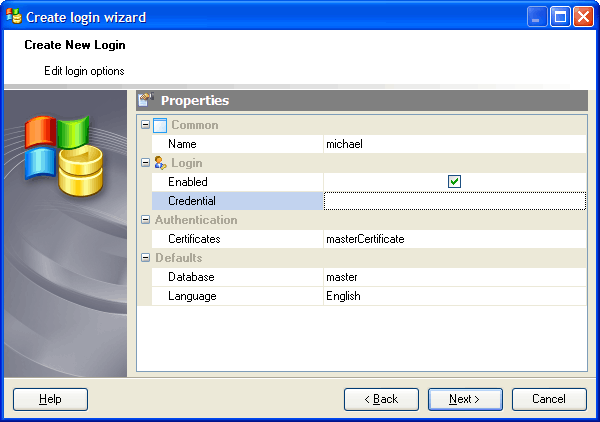
Name
Specifies the name of the Certificate login that is being created.
Note: the name of the object must be unique among all the object names in the server. You can use any identifier that is allowed by Microsoft SQL server.
 Enabled
Enabled
If checked, the login is enabled.
Credential
Define here the name of a credential to be mapped to the new SQL Server login. A credential is a record containing the authentication information required for connecting to a resource outside of SQL Server. The credential must already exist in the server.
Database
Specify the default database to be assigned to the login. The default database is set to MASTER.
Language
Specify the default language to be assigned to the login. The default language is set to the current default language of the server. If the default language of the server is changed in the future, the default language of the login will remain unchanged.
Certificate
Specifies the name of a certificate to be associated with this login. This certificate must already exist in the master database.
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |





 Download
Download Buy
Buy