DB2 Maestro online Help
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |
Specifying type properties
The wizard step was supplied to define common structured type properties. The detailed description of the properties you can find below.
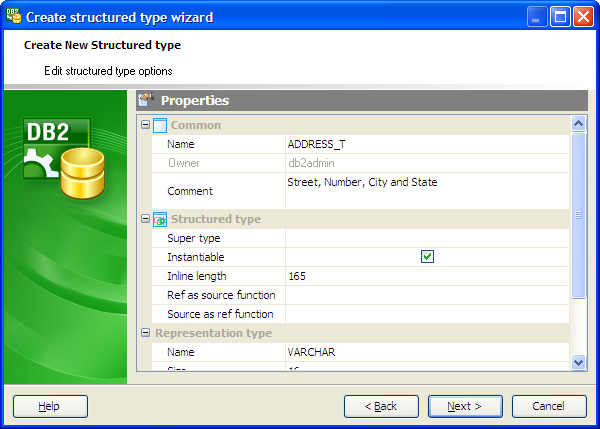
Name
The field represents the new type name as it was set on the previous wizard step. The name, including the implicit or explicit qualifier, must not identify any other type (built-in, structured, or distinct) already described in the catalog. The unqualified name must not be the same as the name of a built-in data type, BINARY, VARBINARY, or BOOLEAN.
Owner
Here you can see the owner of the new structured type. By default, only the owner of an object can perform various operations with the object. In order to allow other users to operate it, privileges must be granted. (However, users that have the superuser attribute can always access any object.)
Comment
Use the field to describe the structured type or leave it blank.
Super type
You can specify here that this structured type is a subtype under the specified supertype-name. The supertype-name must identify an existing structured type. If supertype-name is specified without a schema name, the type is resolved by searching the schemas on the SQL path. This field is not required.
Instantiable
Determines whether an instance of the structured type can be created. Implications of not instantiable structured types are:
| • | no constructor function is generated for a non-instantiable type |
| • | a non-instantiable type cannot be used as the type of a table or view |
| • | a non-instantiable type can be used as the type of a column (only null values or instances of instantiable subtypes can be inserted into the column. |
Inline length
This option indicates the maximum size (in bytes) of a structured type column instance to store inline with the rest of the values in the row of a table. Instances of a structured type or its subtypes, that are larger than the specified inline length, are stored separately from the base table row, similar to the way that LOB values are handled.
Ref as source function
Defines the name of the system-generated function that casts a reference type value for this structured type to the data type rep-type. A schema name must not be specified as part of the function. The cast function is created in the same schema as the structured type. If the clause is not specified, the default value is rep-type (the name of the representation type).
Source as ref function
Defines the name of the system-generated function that casts a value with the data type rep-type to the reference type of this structured type. A schema name must not be specified as part of the function. The cast function is created in the same schema as the structured type. If the clause is not specified, the default value is type-name (the name of the structured type).
Representation type properties:
Source type name
Specifies the data type used as the basis for the internal representation of the distinct type. The source data type cannot be of type XML.
Precision
The first integer is the precision of the number; that is, the total number of digits; it may range from 1 to 31.
BIT data
Specifies that the contents of the column are to be treated as bit (binary) data. During data exchange with other systems, code
page conversions are not performed. Comparisons are done in binary, irrespective of the database collating sequence.
LOBs greater than 1 gigabyte cannot be logged and LOBs greater than 10 megabytes should probably not be logged.
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |





 Download
Download Buy
Buy