ASA Maestro online Help
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |
Create Remote Server Wizard
Create Remote Server Wizard allows you to set up a Remote Server definition. All the information how to run the wizard you can find here.
For ODBC connections, each remote server corresponds to an ODBC data source. For some systems, including SQL Anywhere, each data source describes a database, so a separate remote server definition is needed for each database.
You must have RESOURCE authority to create a remote server.
The basic principles of Create Object Wizards in ASA Maestro are covered by the corresponding topic. See below to find the description of wizard steps that are unique to the current object.
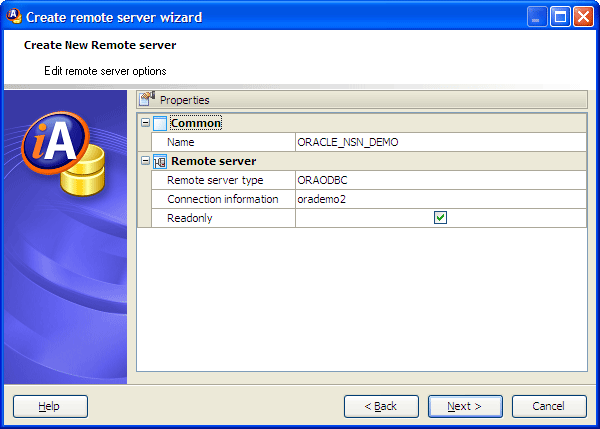
First of all set the new remote server name. It is the name by which the remote server is known within this database.
A remote server type (server class) specifies the server class you want to use for a remote connection. Server classes contain detailed server capability information. There are two groups of server classes. The first is ODBC-based, and the second is JDBC-based.
The ODBC-based server classes are:
| • | saodbc for SQL Anywhere. |
| • | aseodbc for Adaptive Server Enterprise and SQL Server (version 10 and later). |
| • | db2odbc for IBM DB2 |
| • | mssodbc for Microsoft SQL Server |
| • | oraodbc for Oracle servers (version 8.0 and later) |
| • | odbc for all other ODBC data sources |
The JDBC-based server classes are:
| • | sajdbc for SQL Anywhere. |
| • | asejdbc for Adaptive Server Enterprise and SQL Server (version 10 and later). |
Connection information supplies a connection string for the database server. The appropriate connection string depends on the driver being used, which in turn depends on the server-class.
If a JDBC-based server class is used, the connection information is of the form hostname:portnumber [/dbname], where:
| • | hostname The computer the remote server runs on. |
| • | portnumber The TCP/IP port number the remote server listens on. The default port number for SQL Anywhere is 2638. |
| • | dbname For SQL Anywhere remote servers, if you do not specify a dbname, then the default database is used. For Adaptive Server Enterprise, the default is the master database, and an alternative to using dbname is to another database by some other means (for example, in the FORWARD TO statement). |
If an ODBC-based server class is used, the connection information is the data-source-name. The data-source-name is the ODBC Data Source Name.
For SQL Anywhere remote servers (SAJDBC or SAODBC server classes), the connection-info parameter can be any valid SQL Anywhere connection string. You can use any SQL Anywhere connection parameters. For example, if you have connection problems, you can include a LOG connection parameter to troubleshoot the connection attempt.
Read only clause specifies whether the files accessed by the directory access server can be modified.
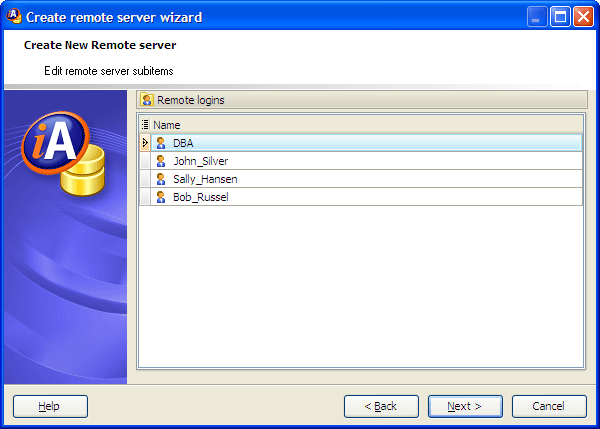
On the next step specify remote logins and their properties. Use the pop-up menu or press Insert to add a new field and set its properties in Create Remote Login Wizard.
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |




 Download
Download Buy
Buy