MS SQL Maestro online Help
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |
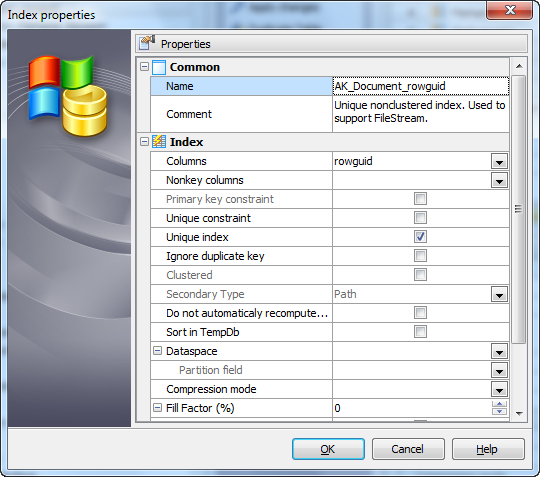
Setting index properties
The Index Properties dialog is available from Create Table Wizard, Table Editor, or from corresponding nodes of the Explorer tree.
Use the Columns drop-down list to select a key field(s) for the index.
 Primary key constraint
Primary key constraint
With this option checked this field becomes a compound primary key. It is useful in case the table has more than one primary key.
 Unique Index
Unique Index
If checked, creates a unique index for the table, i.e. the database system ensures that no two rows of the specified table have the same values in the indexed columns. In this way, if two rows both contain the NULL value for all columns of an index, the two index values are not considered to be identical. If at least one column does not contain the NULL value, two rows that have the same value in all non-NULL columns are considered to be identical.
Constraint
Creates an index on a specified table as a table constraint.
Index
Creates an index on a specified table as database object.
 Ignore duplicate key
Ignore duplicate key
Specifies the error response to duplicate key values in a multiple-row INSERT transaction on a unique clustered or unique nonclustered index. If checked, a warning message is issued and only the rows violating the unique index fail. If not checked, an error message is issued and the entire INSERT transaction is rolled back.
Index Filegroup
If a Filegroup is specified the index is stored in the named filegroup.
Fill Factor
Specifies the percentage that indicates how full the Database Engine should make the leaf level of each index page during index creation or change.
 Pad Index
Pad Index
Specifies index padding. If checked, the percentage of free space portioned by Fill Factor is applied to the intermediate-level pages of the index.
Secondary Type
Specifies the type of secondary XML index.
Create as CLUSTERED
If checked, creates an index in which the logical order of the key values determines the physical order of the corresponding rows in a table.
Do not automatically recompute statistics
If checked, out-of-date statistics are not automatically recomputed.
Primary
Defines primary key.
Sort in TempDB
Specifies whether to store sort results in a TempDB. If checked, the intermediate sort results that are used to build the index are stored in a TempDB.Fill factor
Use the parameter to determine how full the index method will try to pack index pages. For B-trees, leaf pages are filled to this percentage during initial index build, and also when extending the index at the right (largest key values). If pages subsequently become completely full, they will be split, leading to gradual degradation in the index's efficiency. B-trees use a default fill factor of 90, but any value from 10 to 100 can be selected. If the table is static then fill factor 100 is best to minimize the index's physical size, but for heavily updated tables a smaller fill factor is better to minimize the need for page splits. The other index methods use fillfactor in different but roughly analogous ways; the default fillfactor varies between methods.
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |





 Download
Download Buy
Buy