SQLite Maestro online Help
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |
Editing table properties
The Properties section allows you to view general table properties and also to modify the table name.
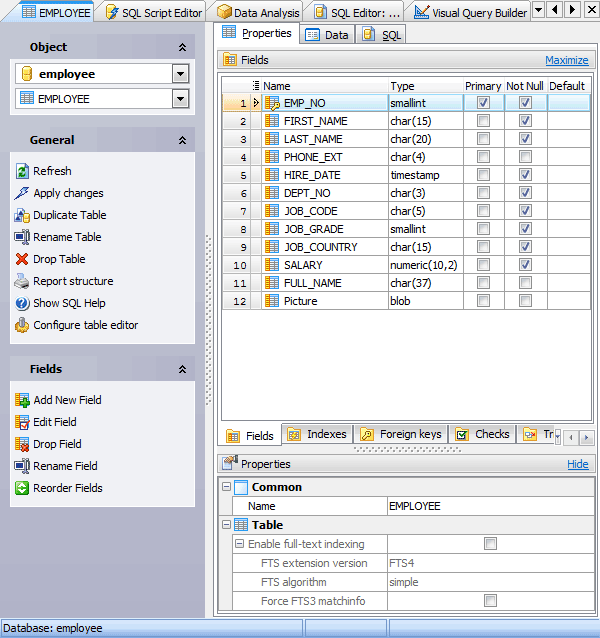
Subitems
Every tab is intended for work with defined objects (fields, indexes, etc.). To modify any object, double click it or use grid’s popup menu. The menu also allows you to add new, rename, describe, copy/paste, and drop selected objects. To operate with several objects at a time, select them with the Shift or the Ctrl key pressed. After a group of objects is selected you can operate with it, e.g. delete several objects at once, as if it is a single object.
The full-text search (FTS) options of the table are represented at the bottom of the editor. If the Enable full-text indexing option is ON, the table is the virtual FTS table that supports a full text search. FTS algorithm contains the FTS tokenizer, a set of rules for extracting terms from a document or basic FTS full-text query, that is used on working with the table. If the Force FTS3 matchinfo box is checked, some of the extra information stored by FTS4 is omitted. Find out more about FTS tables, modules and other such stuff at SQLite documentation.
See also: Fields, Foreign Keys, Triggers, and Indexes.
To apply the changes, select the Apply Changes item in the Navigation bar or use Ctrl+F9 or Ctrl+F7 shortcut keys.
It is also possible to modify object properties without opening the object editor: use the Object Properties item of the popup menu of the selected object from the explorer tree.
| Prev | Return to chapter overview | Next |




 Download
Download Buy
Buy